2-Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazin ist der wichtigste charakteristische Geschmacks-/Aromabestandteil von Paprika. Er kommt auch in frischen Jalapeno-Paprika, Ofenkartoffeln und Wein vor.
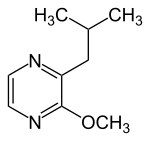
2-Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazin
2-Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazin ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Pyrazine.
Die Verbindung kann durch Kondensation von Leucinamid mit Glyoxal und anschließender Methylierung mit Diazomethan hergestellt werden.
2-Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazin ist eine farblose Flüssigkeit, die in Wasser löslich ist.
- Tim Guildford et al.: The biological roles of pyrazines: evidence for a warning odour function. In: Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. Band 31, Nr. 2, 1987, S. 113–128, doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.1987.tb01984.x.
- [1]Eintrag zu ISOBUTYL-METHOXYPYRAZINE in der CosIng-Datenbank der EU-Kommission, abgerufen am 1. Oktober 2021.
- [2]Datenblatt 2-Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazin, ≥99%, FG bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 23. März 2022 (PDF).
- [3]George A. Burdock: Fenaroli's Handbook of Flavor Ingredients. CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4200-9086-4, S. 993 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- [4]S. Guillaumie, A. Ilg u. a.: Genetic Analysis of the Biosynthesis of 2-Methoxy-3-Isobutylpyrazine, a Major Grape-Derived Aroma Compound Impacting Wine Quality. In: Plant Physiology. 162, 2013, S. 604, doi:10.1104/pp.113.218313.
Questo articolo si basa sull'articolo 2-Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazin dell'enciclopedia libera Wikipedia ed è sottoposto a licenza Licenza GNU per la documentazione libera. Un elenco degli autori è disponibile su Wikipedia.
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | 2-Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazin | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C9H14N2O | |||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
farblose Flüssigkeit | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 166,22 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig | |||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
0,99 g·cm−3 (25 °C) | |||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
214–215 °C | |||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
| |||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,49 (20 °C) | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | ||||||||||||||||

Ricevi il settore delle scienze della vita nella tua casella di posta elettronica
D'ora in poi non perdetevi nulla: la nostra newsletter per il settore alimentare e delle bevande vi aggiorna ogni martedì e giovedì. Le ultime novità del settore, i prodotti e le innovazioni - compatte e facili da capire nella vostra casella di posta elettronica. Studiate da noi per non costringervi a farlo.
