First 3D-bioprinted structured Wagyu beef-like meat unveiled
An environmentally friendly and sustainable method for producing cultured meat alternatives
Advertisement
Scientists from Osaka University used stem cells isolated from Wagyu cows to 3D-print a meat alternative containing muscle, fat, and blood vessels arranged to closely resemble conventional steaks. This work may help usher in a more sustainable future with widely available cultured meat. Wagyu can be literally translated into “Japanese cow,” and is famous around the globe for its high content of intramuscular fat, known as marbling or sashi. This marbling provides the beef its rich flavors and distinctive texture. However, the way cattle are raised today is often considered to be unsustainable in light of its outsized contribution to climate emissions. Currently, the available “cultured meat” alternatives only consist primarily of poorly organized muscle fiber cells that fail to reproduce the complex structure of real beef steaks.
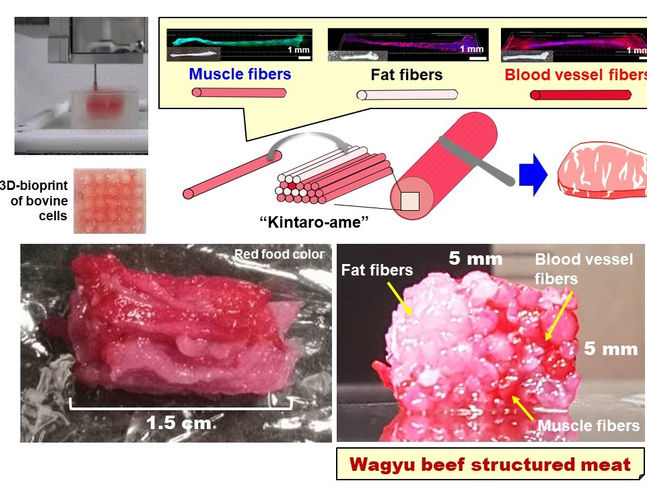
Scheme of structured Wagyu beef meat by “3D printing kintaro-ame technology”
Osaka University
Now, a team of scientists led by Osaka University have used 3D-Printing to create synthetic meat that looks more like the real thing. “Using the histological structure of Wagyu beef as a blueprint, we have developed a 3D-printing method that can produce tailor-made complex structures, like muscle fibers, fat, and blood vessels,” lead author Dong-Hee Kang says. To overcome this challenge, the team started with two types of stem cells, called bovine satellite cells and adipose-derived stem cells. Under the right laboratory conditions, these “multipotent” cells can be coaxed to differentiate into every type of cell needed to produce the cultured meat.
Individual fibers including muscle, fat, or blood vessels were fabricated from these cells using bioprinting. The fibers were then arranged in 3D, following the histological structure, to reproduce the structure of the real Wagyu meat, which was finally sliced perpendicularly, in a similar way to the traditional Japanese candy Kintaro-ame. This process made the reconstruction of the complex meat tissue structure possible in a customizable manner. “By improving this technology, it will be possible to not only reproduce complex meat structures, such as the beautiful sashi of Wagyu beef, but to also make subtle adjustments to the fat and muscle components,” senior author Michiya Matsusaki says. That is, customers would be able to order cultured meat with their desired amount of fat, based on taste and health considerations.
























































